Oily skin is a common concern that affects individuals across all age groups. Characterized by an overproduction of sebum from the sebaceous glands, oily skin can lead to persistent shine, clogged pores, and acne. Understanding oily skin is the first step in addressing its challenges and establishing a skincare routine that balances oil without stripping essential moisture.

Oily Skin Explained: The Basics
Sebaceous glands play a crucial role in maintaining healthy skin by producing sebum—a natural oil that keeps the skin hydrated and protected. However, when these glands become overactive, they can produce excess oil, leading to greasy skin, enlarged pores, and acne. Factors like genetics, hormones, and environmental influences contribute to how much oil your skin produces.
Causes of Oily Skin
Genetics and Heredity
If oily skin runs in your family, you’re more likely to experience it too. Genetics can determine the size and activity level of your sebaceous glands.
Hormonal Changes and Imbalances
Hormonal fluctuations—particularly during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause—can stimulate oil production. Conditions such as PCOS may also contribute.
Environment and Weather Conditions
Hot, humid climates increase perspiration and oiliness. In tropical regions like India, people often experience heightened oil production during summer months.
Diet and Lifestyle Factors
Diets high in refined sugars and dairy may exacerbate oil production. Stress and lack of sleep can also trigger hormonal changes, worsening oily skin.
Skincare Products That Worsen Oiliness
Using overly harsh cleansers or alcohol-based toners can strip the skin of natural oils, causing it to overcompensate by producing more oil.
The Skin Microbiome: A Hidden Factor in Sebum Production
Understanding oily skin requires exploring its relationship with the skin microbiome—the diverse ecosystem of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that live on our skin. Recent research has revealed that the composition of your skin microbiome significantly influences sebum production and overall skin health.
Your skin’s microbiome feeds on sebum, with certain bacteria like Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes) thriving in oil-rich environments. In balanced quantities, these microorganisms can actually help regulate oil production and protect against harmful pathogens. However, when this delicate ecosystem becomes imbalanced, it can trigger inflammation and worsen acne in oily skin types.
Microbiome-Friendly Approaches:
- Gentle Cleansing: Harsh soaps and cleansers don’t just strip away oil—they disrupt beneficial bacteria. pH-balanced cleansers (around 5.5) help maintain healthy microbiome diversity.
- Probiotic Skincare: Products containing prebiotics (food for good bacteria), probiotics (beneficial bacteria), and postbiotics (beneficial bacterial byproducts) can help restore balance to oily skin. Look for ingredients like lactobacillus ferment, bifida ferment lysate, and yogurt extracts.
- Avoid Over-Sanitizing: Constantly using antibacterial products can eliminate beneficial bacteria. Understanding oily skin means recognizing when to control oil versus when to support your skin’s natural ecosystem.
Common Skin Concerns Related to Oily Skin
People with oily skin often struggle with acne, blackheads, and visibly enlarged pores. The excess oil can trap dirt and dead skin cells, leading to clogged pores and breakouts. Over time, repeated inflammation can result in post-acne marks and uneven skin texture.
How to Care for Oily Skin
Gentle Cleansing Twice Daily
Use a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser twice a day to remove dirt and excess oil without disrupting your skin barrier.
Choosing the Right Moisturizer
Opt for lightweight, oil-free moisturizers containing ingredients like hyaluronic acid. These hydrate the skin without adding to the oiliness.
Ingredients to Look For
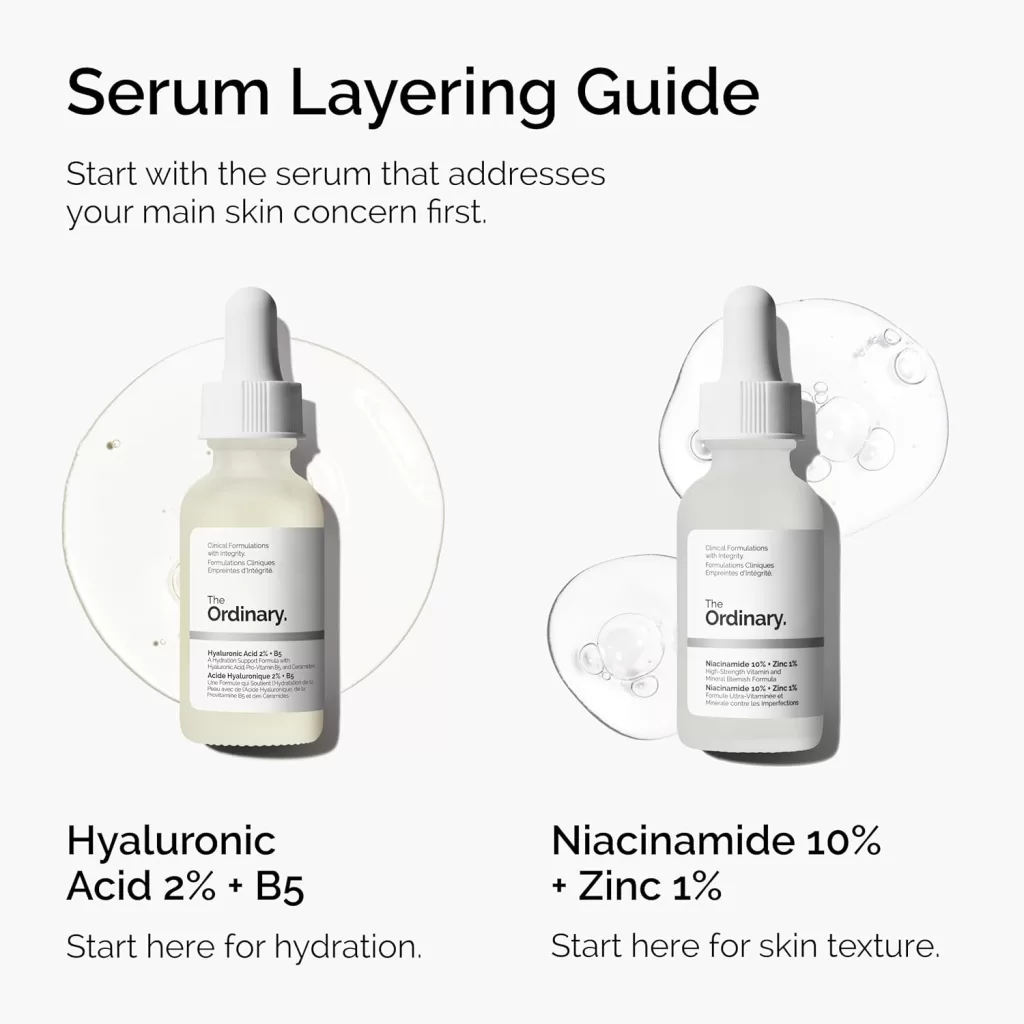
Key ingredients like salicylic acid, niacinamide, and clay are excellent for oily skin. They help regulate oil production, clear pores, and soothe inflammation.
The Importance of Sun Protection
Oily skin still needs SPF. Gel-based, non-comedogenic sunscreens provide protection without clogging pores.
Avoiding Over-Washing or Harsh Products
Avoid scrubbing the skin or washing too often, as it can lead to more oil production and irritation.
Skincare Routine for Oily Skin Types
Morning:
- Cleanser
- Toner (optional)
- Lightweight serum (niacinamide or vitamin C)
- Oil-free moisturizer
- Gel-based sunscreen
Night:
- Cleanser
- Exfoliating toner (2-3 times a week)
- Clay mask (once a week)
- Hydrating serum
- Oil-free moisturizer

Product Recommendations for Oily Skin
| Product | Type | Key Benefit | Price Range | Available In |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Ordinary Niacinamide 10% | Serum | Oil control + clarity | ₹600–₹800 | India, Global |
| Cetaphil Oily Skin Cleanser | Cleanser | Gentle cleansing | ₹400–₹600 | India, Global |
| Neutrogena Hydro Boost Water Gel | Moisturizer | Lightweight hydration | ₹800–₹1000 | India, Global |
| Innisfree Super Volcanic Clay Mask | Mask | Deep pore cleaning | ₹1100–₹1300 | India, Global |
| Minimalist Salicylic Acid 2% | Exfoliant | Anti-acne + decongestion | ₹500–₹700 | India |

Product Recommendations for Oily Skin (USA & EU)
| Product | Type | Key Benefit | Price Range | Available In |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeraVe Foaming Facial Cleanser | Cleanser | Gentle cleansing with ceramides and niacinamide | $15–$20 | USA, EU |
| La Roche-Posay Effaclar Duo+ | Treatment | Targets blemishes and unclogs pores | $30–$36 | USA, EU |
| The Ordinary Niacinamide 10% + Zinc 1% | Serum | Oil control and clarity | $6–$10 | USA, EU |
| Tatcha The Water Cream | Moisturizer | Lightweight hydration with a matte finish | $67–$72 | USA, EU |
| Paula’s Choice Pore-Reducing Toner | Toner | Minimizes pores and balances oil | $25–$30 | USA, EU |
| Differin Adapalene Gel 0.1% | Retinoid | Prevents acne and reduces inflammation | $13–$15 | USA, EU |
| COSRX Acne Pimple Master Patch | Spot Treatment | Protects and heals blemishes | $15 (96 patches) | USA, EU |
| La Roche-Posay Effaclar Shine Control Clay Mask | Mask | Absorbs excess oil and refines pores | $22 | USA, EU |
Myths and Facts About Oily Skin
- Myth: You don’t need moisturizer if you have oily skin. Fact: All skin types need hydration to maintain balance.
- Myth: Scrubbing more reduces oil. Fact: Over-exfoliating irritates the skin and increases oil production.
- Myth: Oily skin means you’re not clean. Fact: Oily skin is a skin type, not a reflection of hygiene.

Hidden Dehydration: When Excess Oil Masks Moisture Loss
Understanding oily skin paradoxes is crucial for effective treatment. One of the most common—yet frequently misdiagnosed—skin conditions is dehydrated-oily skin. This occurs when the skin lacks water (dehydration) but overproduces oil in response, creating a confusing combination of symptoms.
Signs Your Oily Skin Is Actually Dehydrated:
- Skin feels tight after cleansing, yet becomes oily within hours
- Makeup separates or looks patchy despite oiliness
- Fine lines appear more prominent despite excess oil
- Skin appears simultaneously shiny and flaky
- Increased sensitivity and reactivity
How This Happens: When the skin’s moisture barrier becomes compromised (from harsh products, over-exfoliation, or environmental factors), it loses its ability to retain water. The skin responds by producing more oil to prevent further water loss—creating a frustrating cycle where the skin feels oily but is actually crying out for hydration.
Treating Dehydrated-Oily Skin:
- Use hydrating, non-comedogenic ingredients like hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and beta-glucan
- Layer hydration—apply water-based products to damp skin
- Include barrier-repairing ingredients like ceramides and niacinamide
- Avoid harsh astringents and alcohol-based products
- Consider incorporating humectant-rich gel moisturizers rather than completely oil-free formulations
When to See a Dermatologist
If you’re experiencing persistent acne, severe inflammation, or skin that doesn’t respond to over-the-counter products, a dermatologist can provide personalized treatments, including prescription topicals, oral medications, or in-office procedures.
Seasonal Sebum: How Weather Affects Your Skin’s Oil Production
Climate plays a major role in how oily your skin becomes. In hot, humid environments, sebaceous glands become more active. Conversely, in cold, dry conditions, the skin may paradoxically become oilier due to overcompensation. Adjust your skincare accordingly, using oil-absorbing products in summer and barrier-supporting ones in winter.

Navigating Oily Skin Across Different Life Stages
Understanding oily skin requires recognizing how its characteristics and needs evolve throughout different life stages. The approach that works during teenage years won’t necessarily be appropriate in your 30s or 40s.
Adolescent Oily Skin (13-19): During puberty, androgen hormones trigger maximum sebum production, often resulting in the oiliest skin you’ll ever experience. The focus should be on gentle control without over-stripping, as teenage skin is resilient but can develop habits of overproduction if treated too harshly.
Young Adult Oily Skin (20-29): Oil production typically begins to normalize, but stress, hormonal birth control, and lifestyle factors can create fluctuations. This is when understanding oily skin subtypes becomes important—some may develop combination patterns while others remain consistently oily.
Adult Oily Skin (30-45): A crucial transition period where oil production remains significant but other concerns like early signs of aging emerge. The skincare approach needs to balance oil control with hydration and preventative aging care. Many people make the mistake of continuing with the same drying routines from their youth, inadvertently accelerating aging processes.
Mature Oily Skin (45+): While sebum production gradually decreases with age, some individuals maintain oily skin through their 50s and beyond. The challenge becomes addressing both oil control and more pronounced signs of aging—requiring a sophisticated approach that doesn’t compromise either concern.
Hormonal Transitions: Understanding oily skin during significant hormonal events like pregnancy, perimenopause, and menopause requires special consideration. These transitions can create temporary or permanent changes in oil production patterns that necessitate routine adjustments.
By recognizing these life stage variations, you can adapt your skincare approach to address your skin’s current needs rather than treating oily skin as a static condition that never evolves.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Oily Skin
1. What causes oily skin and how can I reduce it?
Oily skin is primarily caused by overactive sebaceous glands producing excess sebum. Common triggers include genetics, hormonal changes, stress, climate, and unsuitable skincare products. To manage it, use gentle cleansers, oil-free moisturizers, and active ingredients like niacinamide or salicylic acid.
2. Can oily skin still be dehydrated?
Yes! Oily skin can lack water and still feel greasy. This condition is known as dehydrated oily skin, and it’s best addressed by using hydrating serums (like hyaluronic acid) while avoiding alcohol-heavy or overly stripping products.
3. What are the best products for oily skin in India and globally?
Some highly recommended options include:
- The Ordinary Niacinamide 10% (oil control)
- Cetaphil Oily Skin Cleanser (gentle daily cleanser)
- Neutrogena Hydro Boost Gel (hydration without heaviness)
These are easily available in both Indian and global markets. For exfoliation, Minimalist’s Salicylic Acid 2% is a strong local choice.
4. Does oily skin need sunscreen daily?
Absolutely. Oily skin still requires sun protection to prevent dark spots, premature aging, and oil-triggered damage. Use gel-based or mattifying sunscreens labeled non-comedogenic—they won’t clog pores or worsen acne.
5. How do I build a skincare routine for oily skin?
Your routine should include:
- AM: Gentle cleanser → oil-control serum → lightweight moisturizer → SPF
- PM: Cleanser → exfoliating toner (2–3x/week) → treatment serum → oil-free moisturizer
Add a clay mask once a week for deep pore care.
6. Which ingredients should I avoid if I have oily skin?
Avoid ingredients like mineral oil, lanolin, petroleum, and drying alcohols. These can either clog pores or strip the skin too much, worsening oiliness over time.
7. When should I see a dermatologist for oily skin?
If you’re experiencing persistent acne, excessive shine, or texture issues that don’t improve with over-the-counter skincare, consult a dermatologist. They can recommend prescription treatments or peels tailored to oily-prone skin.

Conclusion
Understanding oily skin is crucial to managing it effectively. By identifying its causes and implementing a balanced skincare routine, you can reduce shine, prevent breakouts, and improve your overall skin texture. Consistency, the right products, and informed care make all the difference.
✨ Discover More at Where & How Resources
Looking for expert tips on oily skin, honest product reviews, or simple skincare routines that actually work?
Visit WhereAndHowResources.com — your trusted destination for all things beauty and skincare.
We bring you:
- 🧴 Tried-and-tested routines for every skin type
- 🌿 Natural and Ayurvedic remedies that deliver results
- 💬 Real answers from real users, inspired by Quora’s most asked questions
- 💸 Smart shopping tips and budget-friendly product comparisons
- 🧠 Science-backed insights explained in everyday language
Your glow-up starts with knowledge. Let us guide you there.