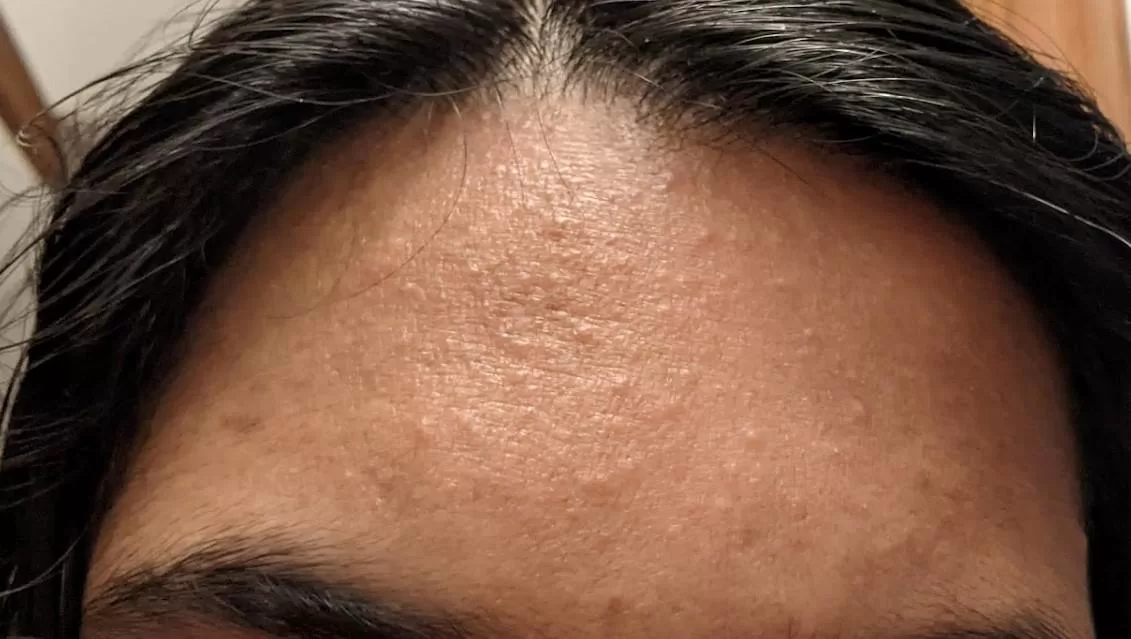
Understanding and Treating Long Bumps on the Forehead: Effective Skincare Solutions
Those pesky long bumps on your forehead can be a real puzzle! They could be from clogged pores, acne, or even a skin condition. Figuring out what’s causing them is the first step to getting rid of them. This guide will help you understand your options and find the best way to treat those annoying bumps. Explore all Forehead bumps treatment products below.
Identifying the Cause of Forehead Bumps

The first step in treating long bumps on the forehead is to determine their cause. Here are some common culprits:
- Acne or Comedones: Caused by clogged pores, these bumps are often firm and flesh-colored, typical in areas with active oil glands.
- Fungal Infections (Malassezia Folliculitis): Often mistaken for acne, this condition results from yeast overgrowth on the skin. The bumps are uniform, may be itchy, and don’t respond to traditional acne treatments.
- Keratosis Pilaris: This condition leads to small, rough bumps, caused by a buildup of keratin. Though more common on the arms and thighs, it can appear on the forehead.
- Dermatitis or Allergic Reactions: Sensitive skin may react to certain products with bumps, redness, or itching.
How Hormonal Fluctuations Influence Acne Development on the Forehead
Hormonal fluctuations play a significant role in the development of acne, including on the forehead. Throughout different stages of life, such as puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, the body undergoes various hormonal shifts. These changes can increase the production of sebum, an oily substance produced by the skin’s sebaceous glands.
The Role of Sebum
- Sebum Overproduction: When hormone levels fluctuate, especially with an increase in androgens, it can lead to excessive sebum production. This surplus oil can mix with dead skin cells and clog pores, creating a breeding ground for acne-causing bacteria.
Localized Impact on the Forehead
- Forehead Susceptibility: While hormonal acne is often associated with the lower face, fluctuations can also trigger breakouts on the forehead. Since this area is part of the T-zone, which is naturally oilier, it becomes more prone to such outbreaks when hormone levels spike.
Hormonal Changes and Breakouts
- Puberty: This is a period marked by a surge in hormones, making teenagers particularly vulnerable to acne on the forehead.
- Menstrual Cycle: Many women experience breakouts before their cycle begins due to hormonal imbalances.
- Pregnancy and Menopause: These life stages bring about dramatic hormonal shifts, which can lead to a sudden increase in forehead acne.
Understanding how these hormonal changes affect your skin can be the first step in managing acne effectively. Recognizing the patterns can help in seeking appropriate treatments to maintain clearer skin.
What Medications Can Aggravate Acne?
Acne can sometimes be worsened by certain medications, making it crucial to be aware of what you’re taking. Here’s a rundown of some medications known to potentially trigger or exacerbate acne:
- Hormonal Medications: Certain birth control pills, particularly those that are progesterone-dominant, can lead to acne flare-ups.
- Steroids: Corticosteroids, often used for their anti-inflammatory properties, have been linked to acne, commonly referred to as “steroid acne.”
- Vitamin Supplements: High doses of vitamin B-12 supplements have been associated with the development of acne in some individuals.
- Anticonvulsants: These drugs, used primarily to treat seizures, have also been reported to induce acne as a side effect.
If you suspect your medication is affecting your skin, consult with a healthcare provider for tailored advice. Making adjustments under medical guidance might help manage these unwanted effects without compromising your health.
Understanding the Causes of Acne-Related Inflammation
Inflammation is a key factor in the development of various types of acne lesions. But what triggers this inflammation? Let’s dive into some of the main contributors:
Hormonal Changes
Throughout life, hormones can fluctuate due to events like puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause. These fluctuations often trigger oil production in the skin, leading to inflammation and acne in various areas, including the forehead.
Stress
When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones that can aggravate your skin and lead to breakouts. There’s also evidence suggesting stress can disturb your gut microbiota, which plays a role in skin health.
Medications
Certain medications can provoke acne by disrupting your body’s chemistry. For instance, some types of birth control pills and systemic medications like corticosteroids, vitamin B-12, and anticonvulsants can lead to acne-related inflammation.
Hair and Skin Products
Products with comedogenic (pore-clogging) ingredients might be causing issues if you’re experiencing acne, particularly around the hairline. Review the ingredient lists on your haircare products and avoid those known to clog pores.
Diet
What you eat can significantly impact your skin. Diets high in sugar and refined carbs (foods with a high glycemic index) are linked to increased acne inflammation. On the other hand, omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish may help reduce acne-related inflammation.
Key Takeaways
Understanding these factors can help you identify what’s behind your acne. Adjusting lifestyle choices and being mindful of dietary and product selection may assist in reducing inflammation and improving skin health.
Wearing headbands or hats, especially those with tight bands or brims, can contribute to acne in several ways. The main culprit is friction, which occurs when these accessories continuously rub against your skin, particularly on the forehead. This irritation can inflame the skin, leading to the development of blemishes.
Additionally, when headbands or hats trap sweat and oil, it creates an environment conducive to acne-causing bacteria. The combination of warmth and moisture under these accessories can exacerbate clogged pores, resulting in breakouts.
To minimize these effects, consider opting for breathable materials when choosing headgear. Regularly washing your accessories can also help prevent the buildup of sweat and oils. If you’re prone to acne, it might be beneficial to reduce the time you spend wearing such items.
How Hair Products Can Lead to Forehead Acne Bumps
Hair products often go unnoticed as a potential cause of those pesky bumps on your forehead. But let’s dive into how they might be the culprits behind forehead acne.
The Role of Comedogenic Ingredients
Many hair care products contain ingredients known to clog pores, known as comedogenic ingredients. When these products come into contact with your skin, especially around the hairline, they can trap dirt and oil, leading to breakouts.
Transfer of Oils from Hair to Skin
Even if you don’t have oily hair, certain styling products or conditioning treatments can transfer oils to your forehead. These products create a barrier on the skin’s surface, preventing it from breathing and often exacerbating acne formation.
Sweat and Product Build-up
If you’re active or spend a lot of time outdoors, sweat combined with hair product residue can further clog pores. This is especially true if you wear headgear like hats or headbands, which can trap these substances against your skin.
Ingredients to Watch Out For
To reduce the risk of acne caused by hair products, avoid ingredients that are known to block pores. Be cautious of:
- Petrolatum: Often found in moisturizers and hair lotions
- Coconut oil: Great for hair, but not so much for acne-prone skin
- Isopropyl myristate: Common in conditioners and known for high comedogenicity
Switching to non-comedogenic products designed to be gentle on the skin might help reduce forehead acne. Regularly cleansing your skin, especially around the hairline, can also prevent breakouts.
When it comes to understanding acne, it’s essential to recognize the various types of lesions, each with distinct characteristics. Here’s a breakdown of the different types of acne lesions frequently described in medical terms:
1. Comedones
These occur when pores get clogged by dead skin cells and oil. They are classified into:
- Whiteheads (Closed Comedones): Appear as small bumps beneath the skin.
- Blackheads (Open Comedones): Present as dark, visible spots on the skin surface due to exposure to air.
2. Papules
Papules arise when blocked pores become irritated or inflamed, resulting in red, tender bumps on the skin.
3. Pustules
These are similar to papules but filled with pus, making them appear as red, inflamed lesions with a white or yellow center.
4. Nodules
Nodules are large, painful lumps that form deep within the skin, often feeling hard to the touch. They are more severe and can lead to scarring.
5. Cystic Acne
This type involves deep, pus-filled pockets beneath the skin’s surface. It’s a severe form of acne that can occur on the forehead and other facial areas. Dermatologists sometimes use cortisone injections to reduce these lesions.
6. Fungal Acne
Not typical acne, this type of folliculitis is caused by a yeast infection. It manifests as small, uniform bumps and can appear on the forehead, hairline, chest, and back, triggered by a naturally occurring skin fungus.
Understanding these various types helps in identifying and selecting the appropriate treatment for acne.
Building an Effective Skincare Routine
Once you’ve identified the cause, a consistent skincare routine can help manage and reduce forehead bumps. Here’s how to get started:
1. Gentle Cleansing

Cleansing is the foundation of any skincare routine, especially when dealing with bumps.
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a non-comedogenic cleanser twice daily to remove excess oil, dirt, and makeup. Consider cleansers with salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide if acne is the issue.
- Avoid Over-Cleansing: Over-washing can strip natural oils, leading to increased oil production and potentially more bumps.
Recommended Product:
- CeraVe Foaming Facial Cleanser: Contains niacinamide and ceramides, suitable for oily and combination skin.

CeraVe Hydrating Cream – to – Foam Cleanser for Normal to Dry Skin with Amino Acids, Hyaluronic Acid and 3 Essential Ceramides, 236 ml
2. Targeted Topical Treatments
Topical treatments can address specific causes of forehead bumps:
- Salicylic Acid: Exfoliates the skin and clears pores, ideal for acne-related bumps.
Salicylic Acid Concentrate Super Strong 2% – Acne Spot Treatment – Professional Skincare Serum
- Benzoyl Peroxide: Reduces acne-causing bacteria and inflammation.

Acnecide Face Gel 5% Benzoyl Peroxide Acne Treatment for Spot Prone Skin 15g
- Azelaic Acid: Treats both acne and rosacea by clearing pores, reducing inflammation, and brightening skin.

Azelaic Acid Suspension 10% Face Serum,Azelaic Acid Serum Cream,Face Skin Care Beauty with Niacinamide & Vitamin C,Reduces Blackheads,Removes Acne..
- Retinoids: Promote cell turnover to prevent clogged pores, starting with a low concentration to avoid irritation.

CeraVe Retinol Serum for Post-Acne Marks and Skin Texture | Pore Refining, Resurfacing, Brightening Facial Serum with Retinol | 1 Ounce
- Antifungal Creams: For fungal acne, antifungal treatments like ketoconazole or clotrimazole are more effective than traditional acne treatments.

Daktarin Intensiv Cream Ketoconazole 15g
Recommended Products:
- Paula’s Choice Skin Perfecting 2% BHA Liquid Exfoliant: Salicylic acid-based exfoliant for clogged pores.
- The Ordinary Niacinamide 10% + Zinc 1%: Reduces oil production and calms skin.
- Differin Gel (Adapalene): An over-the-counter retinoid for acne treatment.
- Nizoral Anti-Dandruff Shampoo: Can be used as a mask for fungal acne.
3. Exfoliation
Exfoliating helps to prevent clogged pores and smooth out skin texture:
- Chemical Exfoliation: Use exfoliants with alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs) 1-2 times per week to avoid irritation.
- Physical Exfoliation: Be cautious with scrubs as they can irritate the skin and worsen the condition.
4. Moisturizing

Moisturizing keeps your skin hydrated and balanced:
- Non-Comedogenic Moisturizers: Opt for light moisturizers that won’t clog pores. Ingredients like hyaluronic acid and niacinamide soothe and reduce inflammation.
- Avoid Pore-Clogging Ingredients: Steer clear of products containing coconut oil or heavy pomades, which are known to clog pores and exacerbate acne. These ingredients are often found in haircare products, so be mindful of what you’re applying to your scalp and hair.
- Check Your Hairline: Breakouts can often occur along the hairline due to transfer from hair products. Make it a habit to cleanse this area thoroughly to prevent acne.
- By integrating non-comedogenic products into both your skincare and haircare routines, you can effectively manage and reduce breakouts, promoting clearer, healthier skin.
Recommended Product:
- CeraVe Moisturizing Cream: A hydrating, non-comedogenic option that strengthens the skin barrier.
5. Sun Protection

Protecting your skin from the sun is essential, as UV exposure can worsen skin conditions and lead to pigmentation issues:
- Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen: Use a non-comedogenic sunscreen daily to shield your skin from harmful UV rays.
Recommended Product:
- La Roche-Posay Anthelios Melt-in Milk Sunscreen SPF 60: Offers broad-spectrum protection and is gentle on the skin.
Forehead bumps treatment
How Hair Products with Comedogenic Ingredients Affect Forehead Acne
Hair products can play a surprising role in the development of forehead acne, largely due to the presence of comedogenic ingredients. These ingredients have a tendency to clog pores, which can lead to breakouts, particularly along the hairline. When you use shampoos, conditioners, or styling products, these substances can transfer to your forehead, trapping oil and bacteria on the skin.
What to Watch For
If you’re experiencing acne on your forehead and you don’t regularly wear hats, headbands, or helmets, your hair products might be the culprit. Look for these common comedogenic ingredients:
- Coconut oil
- Shea butter
- Sodium lauryl sulfate
- Mineral oil
Steps to Take
To minimize the impact of these ingredients on your skin, consider switching to non-comedogenic hair products. Check product labels and opt for formulations that mention being suitable for sensitive or acne-prone skin. Regular cleansing of your forehead area can also help keep pores unclogged, reducing the risk of breakouts.
By being mindful of the products you use, you can maintain healthier skin and potentially reduce forehead acne.
When to See a Dermatologist
Dealing with persistent forehead bumps requires a comprehensive approach. Regular exercise can contribute to overall skin health, but it’s essential to combine it with targeted skincare. Identifying the root cause of the bumps is key to effective treatment. While over-the-counter products may help, for forehead bumps treatment, consider consulting a dermatologist if they worsen or fail to improve. Dermatologists can provide prescription medications, chemical peels, laser therapy, or extractions tailored to your specific skin condition.
How Touching Acne-Prone Areas with Your Hands Affects Skin Health
Touching your face, especially areas prone to acne, can significantly impact your skin’s health. Here’s how:
- Transfer of Bacteria: Your hands come into contact with countless surfaces throughout the day, collecting bacteria and dirt. When you touch your face, these impurities are transferred to your skin, potentially leading to clogged pores and breakouts.
- Oil Spread: Your hands naturally produce oils, which can transfer to your face when touched. This additional oil can contribute to the overproduction of sebum, making acne worse in oily areas such as the forehead.
- Irritation and Inflammation: Constantly touching or picking at blemishes can irritate the skin, causing redness and inflammation. This can make acne more noticeable and prolong the healing process.
- Unconscious Habits: Many people touch their faces without even realizing it—whether it’s brushing hair away or resting their chin on their hand. Becoming aware of these habits is crucial to maintaining healthier skin.
Incorporate simple habits like regularly washing your hands and using tissues or clean cloths instead of bare hands when necessary. This can prevent the transfer of unwanted materials onto your face and help maintain a clearer complexion.
How Hair Length and Style Affect Forehead Acne
When it comes to forehead acne, your hair length and style can have a significant impact, either by contributing to breakouts or by concealing them.
Hair Oils and Acne
Long hair, especially when styled forward, can introduce natural oils from the hair onto the skin. This extra oil can clog pores, leading to acne flare-ups. If you notice more breakouts, consider styles that keep hair away from the forehead to minimize contact.
Bangs and Concealment
Bangs may seem like a quick fix to hide existing acne, but they can exacerbate the issue. While they effectively mask blemishes, they can trap sweat, oil, and dirt against the skin, creating an environment ideal for acne development.
Styling Tips
If you have lengthy locks, it’s beneficial to opt for hairstyles that pull the hair back. Here are some suggestions:
- Ponytails or Buns: Simple yet effective in keeping hair off the face.
- Headbands or Clips: Useful for keeping bangs at bay without drastic styling changes.
- Layered Cuts: Consider a style that naturally sweeps hair away from the forehead.
In short, being mindful of hair styles and ensuring that hair is kept clean can help in managing and potentially reducing forehead acne.
Why Is Popping a Pimple Not Recommended?
Popping a pimple might seem like a quick fix, but it can lead to several unwanted consequences.
1. Increased Risk of Infection
When you squeeze a pimple, you break the skin, making it vulnerable to bacteria. Although infection might not be common, even a minor one can cause redness and pain.
2. Potential for Skin Damage
Squeezing pimples can push trapped oil, bacteria, and dead skin deeper into your pores. This action might lead to more severe acne issues rather than solving them.
3. Unwanted Scarring and Discoloration
Repeated pimple popping can result in scars or dark spots, which can be more challenging to treat than the pimple itself. By leaving the pimple alone, you give your skin a better chance to heal naturally without long-term marks.
Instead, consider using topical treatments that target acne without causing damage. Options range from over-the-counter solutions featuring salicylic acid to more advanced treatments like retinoids, which promote healthier skin turnover.
In essence, patience and proper skincare are your best allies against acne, allowing your skin to heal effectively without unnecessary damage.
Diet and Lifestyle Considerations

Meals That Heal: 100+ Everyday Anti-Inflammatory Recipes in 30 Minutes or Less: A Cookbook
Beyond skincare, lifestyle changes can also help reduce forehead bumps:
- Balanced Diet: Limit dairy and high-glycemic foods, which can trigger acne. Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids. While research hasn’t pinpointed the “best” diet for skin health, maintaining a well-rounded and nutritious diet supports your body’s optimal functioning, which in turn can lead to healthier skin.
- By reducing intake of potential acne triggers like dairy and sugary foods, you allow your skin to benefit from the nutrients found in whole foods. Emphasizing fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids not only nourishes your body but also helps in managing acne more effectively. It’s important to remember that the relationship between diet and acne is complex, and individual responses can vary. However, a balanced diet is a powerful tool in your skincare arsenal.
- Stress Management: Forehead bumps treatment involves a comprehensive approach. Regular exercise can improve overall skin health, but it’s crucial to identify and address the root cause of the bumps. Stress can exacerbate acne, so incorporate practices like yoga, meditation, or regular exercise into your routine.
- Stress releases hormones that can lead to breakouts by increasing oil production in your skin. Additionally, stress can upset your gut microbiota, which may contribute to acne development. Understanding these biological impacts highlights the importance of managing stress effectively to maintain clear skin. By addressing stress through healthy lifestyle choices, you can help mitigate these internal triggers and support your skin’s health from the inside out.

FAQs: Forehead bumps treatment
- What are the most common causes of forehead bumps?
- Acne (clogged pores)
- Fungal infections (Malassezia folliculitis)
- Keratosis pilaris
- Dermatitis or allergic reactions
- What are the key steps in a skincare routine for forehead bumps?
- Gentle cleansing
- Targeted topical treatments (salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, etc.)
- Exfoliation (chemical and/or physical)
- Moisturizing
- Sun protection
- What lifestyle factors can contribute to forehead bumps?
- Diet (limiting dairy and high-glycemic foods)
- Stress management (exercise, yoga, meditation)
- When should I see a dermatologist?
- If forehead bumps persist or worsen despite home care
- If you’re unsure of the cause of the bumps
Key Takeaways
- Identifying the root cause of forehead bumps is crucial for effective treatment.
- A consistent skincare routine with gentle cleansing, targeted treatments, and moisturization is essential.
- Lifestyle factors like diet and stress management can play a significant role.
- Consulting a dermatologist is recommended for persistent or severe cases.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional 1 for any health concerns or before making any decisions regarding your health or treatment.
Conclusion: Forehead bumps treatment
Dealing with persistent forehead bumps can be frustrating. To clear them up, you need to figure out what’s causing them and create a skincare routine that works for you. Using the right products and making healthy lifestyle choices can help a lot. But if your skin isn’t improving, it’s a good idea to see a dermatologist for expert advice.
Explore more articles like this @ Where And How Resources